

While one can observe fire occurrences, these occurrences are difficult to predict as the large majority of events are ignited by humans due to negligence or arson. Remotely sensed observations, on the other hand, have been available for decades but fire activities have only been reliably monitored since early 2000. As such, it cannot be used to derive long term statistics. This is an on-demand service, available since 2014, that can only be activated by authorised users and relies on limited resources (there is a limit on the number of multiple simultaneous activations that can be processed). The catalogue is linked to the Copernicus Emergency Management Service, which provides timely geospatial information in support of emergency management activities following a disaster. The Joint Research Centre Data Catalogue ( ) tries to overcome this issue by collecting, in a single data portal, information about wildfires in Europe (amongst other natural or man-made disasters). As such, they are often only available in the local language and use different standards for data collection making the information fragmented and unevenly distributed over the globe. On the one hand, event catalogues are collated by local authorities. However, fire observations present a number of limitations. Indeed, the fire community would benefit from more data on fire observations 3 to characterise temporal trends as well as identify and quantify impacts on population, ecosystems and infrastructures. Longer fire seasons, more extreme fire weather and more rain-free days globally are inducing significant variations in wildfire danger 2.
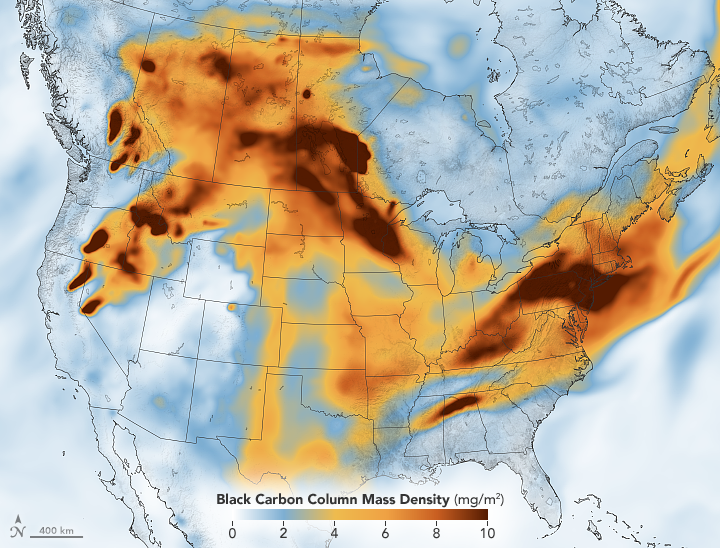
#Nasa fire map canada free
The global dataset is produced by ECMWF, as the computational centre of the European Forest Fire information System (EFFIS) of the Copernicus Emergency Management Service, and it is made available free of charge through the Climate Data Store.įorest fires are an integral part of the natural Earth system dynamics, however they are becoming more devastating and less predictable as anthropogenic climate change exacerbates their impacts 1. It is a valuable resource for forestry agencies and scientists in the field of wildfire danger modeling and beyond. The new fire danger reanalysis dataset provides a number of benefits compared to the one based on ERA-Interim: it relies on better estimates of precipitation, evaporation and soil moisture, it is available in a deterministic form as well as a probabilistic ensemble and it is characterised by a considerably higher spatial resolution. This manuscript describes a reanalysis dataset of fire danger indices based on the Canadian Fire Weather Index system and the ECMWF ERA5 reanalysis dataset, which supersedes the previous dataset based on ERA-Interim. In order to advance fire science, fire danger reanalysis products can be used as proxy for fire weather observations with the advantage of being homogeneously distributed both in space and time. Forest fires are an integral part of the natural Earth system dynamics, however they are becoming more devastating and less predictable as anthropogenic climate change exacerbates their impacts.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
